More CSS
Different stylesheets produce different styles of your HTML page.
Here is a demo provided by W3School. Click to try it.
CSS syntax
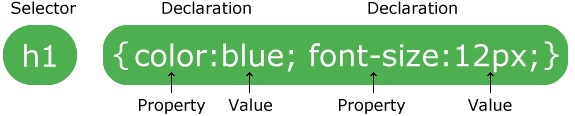
Selectors
- element selector : use element name, like
h1,p,span... - id selector : set
id="idname"in element, then use#idnameto select it, id should be unique - class selector : set
class="clsname"in element, then use.clsnameto select it
Example - HTML Part:
<div id="myid">
This block has id equal to <span>myid</span>.
</div>
<div class="course">
In this course, you will learn the following topics:
...
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
Example - CSS Part:
span {
background: #dddddd;
color: red;
}
#myid {
background: lightyellow;
color: blue;
}
.course {
background: lightgreen;
color: black;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Result:
Box model properties
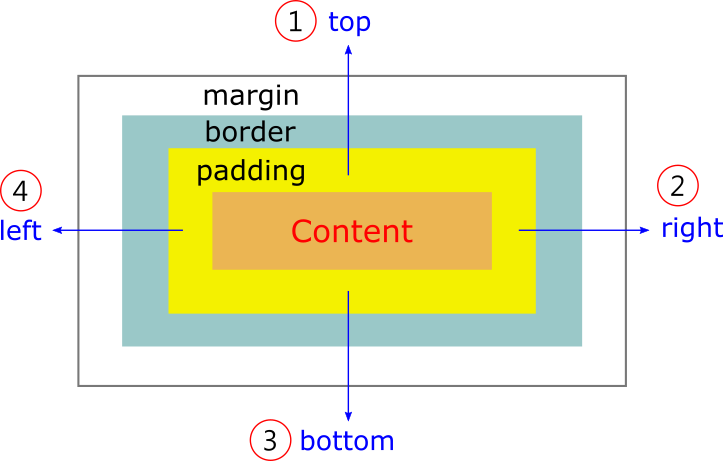
For block-level elements (like div), you can set the following properties:
width: Set the width of the contentheight: Set the height of the contentpadding: Set the padding propertiesborder: Set the border propertiesmargin: Set the margin properties
Note:
- For
widthandheight, use px or ratio, like:
height: 200px;orwidth: 80%. - For
padding,borderandmargin, use the following syntax:keyword: top right bottom leftto set 4 parameters, ex:padding: 12px 6px 8px 4px;keyword: parato set 4 parameters (all equal to para), ex:padding: 12px;keyword: para1 para2;to set 4 parameters, para1 will be set for top and bottom, para2 will be set for right and left, ex:margin: 12px 4pxormargin: 12px auto. (set left and right to auto to align it to center)keyword-direction: parato set a single parameter, ex:margin-top: 12px;- Border is usually set with other properties, ex:
border: 2px solid green;
Example:
Exercise
Add more HTML and CSS contents to your web page.